Academic Fields in Finance
- Dobromir Risov
- Sep 24, 2025
- 5 min read
Updated: Nov 6, 2025

Introduction to academic fields in finance
I present a brief review of finance theories starting in the 1800s. I describe two theories in more detail. One from each "camp": traditional & behavioural finance. There are more relevant models used by professionals but not relevant for an individual investor. Every model following is grounded in those mentioned here. I also chose the picture above to show the sheer number of models and aspects to consider. I provide a context how important these models are for an individual investor so he is not left alone with the information.
Main
The term finance refers to how businesses raise capital to finance their operations. It´s from the point of view from those who need capital. The term investment is on the other side of the same coin: it´s from the point of view of those who have funds and look for ways to give it to a business in exchange for a decent return. Often one term is used but it covers both areas.
In Finance there is the school of traditional finance and that of behavioural finance. Traditional finance theories are grounded in the expected utility theory originating in the 1800s. The theory was developed by John Stuart Mill. Mill´s theory builds upon three important assumptions: perfect rationality, perfect self-interest and perfect information. The common denominator is perfect. You probably realise by now the weakness of this theory. Closely related to this theory is the homo oeconomicus. With theories it´s about testing them how well they explain reality.
Roughly one century later, in the 1950s Harry Markowitz developed the famous portfolio theory. Harry Markowitz who died in 2023, is one of the most famous scolars in traditional finance. His theory is about expected return and risk of a portfolio. That portfolio consists of many securities. When you look at the graph below - have a look at the efficient frontier: at the efficient frontier lie all the optimal portfolios. There are portfolios below and above the efficient frontier but they are not the best possible choice for an investor who follows Markowitz´s model. Optimal is defined in two ways:
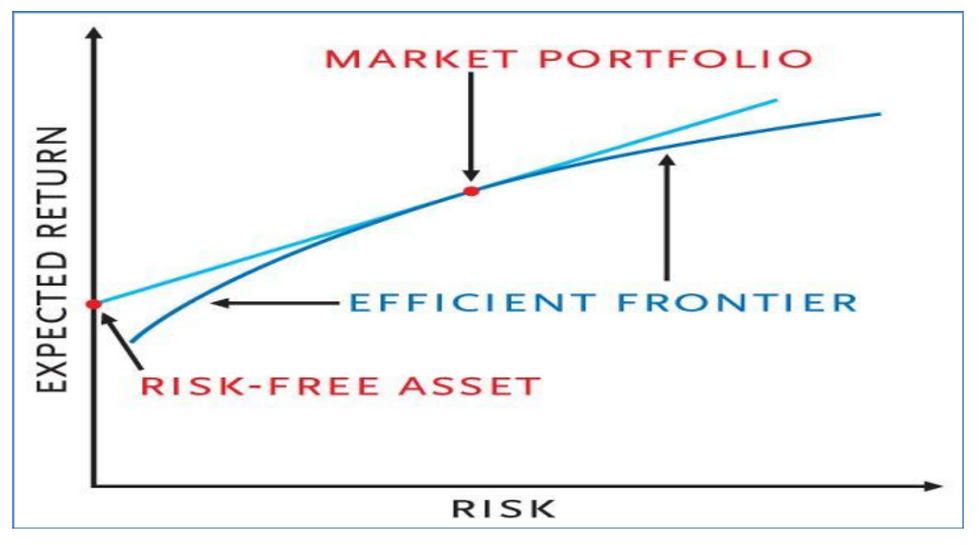
“the concept of the efficient frontier represents the set of portfolios that offer the highest expected return for a given level of risk or the lowest risk for a given
level of expected return”
For example if I as an investor want to tolerate a maximum of 15% risk in my portfolio, I will look for a portfolio which offers the highest return at a 15% level of risk. That makes sense. In very simple words, if I don´t want to spend more than 1€ for a chocolate, then I will go and look for the best value of chocolate for 1€. Back to portfolios - I find that portfolio on the efficient frontier. Risk is measured as standard deviation, a statistical term. It´s calculated using past stock returns. Bear in mind: That is, on average my selected portfolio should not fluctuate by more than 15%. Still the portfolio can fluctuate by more than 15% in reality: Markowitz uses past data to serve as a guideline for the future, something common in finance. He was also awarded the Nobel prize in 1990.
Eugene Fama is another very important scolar in the field of traditional finance About 20 years after Markowitz, Eugene Fama developed the efficient markets hypothesis, in the 1970s. My research reveals Eugene Fama is also a founding member of the investment fund company Dimensional. He too was awarded the Nobel prize in 2013.
Theories are tested in reality to see how good they describe reality. The need for behavioural finance stems from the inability of traditional finance to deal with "anomalies" in the financial markets. Anomaly is another term for irrational behaviour by investors. Examples for such behaviour are the Tulip Mania, the South Sea bubble or the Mississipi bubble. You find an article here on Tulip Mania. How does one explain those anomalies? Scolars in behavioural finance try to do that.

„Behavioural finance relates to the psyche
of investors and its role in decision making”.
Around the mid 1950s at the height of traditional finance, scolars of behavioural finance start to do their work. Kahnemann & Tversky are probably the most prominent scolars . Kahneman was awarded the Nobel prize in 2002 for his work on prospect theory, he had developed with Tversky. The prospect theory´s cornerstone is the idea of loss aversion. That means people choose to avoid losses rather than make gains. People are more afraid of losses than interested in gains. For example the value of winning 100€ is less appealing to me than avoiding the loss of 100€. I hurt more emotionally losing 100€ than I am happy about winning 100€. This is shown in the graph below: The curve flattens with the prospect of a higher gain, but it decreases more with the prospect of losing the equivalent amount. In prospect theory, emotions are also accounted for in the process of decision making.

For you as an investor you need not apply any of those models. In practice the models serve as a guideline for finance professionals. Markowitz´s portfolio is used to advocate diversification of investments. Further it´s useful to understand what return and risk are in this model. It's also important to understand no business or accounting information is used. The assumption is that whatever information there is out there - that includes the aforementioned areas is incorporated in the stock price. For example stock whose price fluctuates little – are less risky in the language of traditional finance. These models are meant for academic research rather than a hands on toolkit. For an individual investor the important advice is to diversify.
Summary
There are two schools in finance - traditional and behavioural The theoretical models in traditional finance can´t explain anomalies exhibited in the day to day of financial markets. I talk of anomalies. Anomalies are events where investors behave "irrationally". Scolars of behavioural finance developed models to explain those irrational events.
Individual investors need not understand the models in detail to do well as investors. Yet it´s useful for individual investors to know how risk and return are defined and about the limitations. When you look at both graphs you recognise Markowitz portfolio theory is entirely technical. The prospect theory by Kahnemann & Tversky accounts for financial and emotional aspects..
Sources:
Behavioural Finance: A Review (Kapoor & Prosad)
What is Modern Portfolio Theory? (Certificate in Quantitative Finance)
Pictures:
Efficient Frontier, https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Market-Portfolio-Efficient-Frontier_fig1_259075987
Eugene Fama, https://news.uchicago.edu/profile/eugene-fama
Prospect theory, https://www.invespcro.com/blog/prospect-theory/
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1.What are the main academic fields in finance?
The two key branches are Traditional Finance, which assumes entirely rational decision-making, and Behavioral Finance, which studies how emotions influence decision making of investors.
2. What is the Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH)?
Developed by Eugene Fama, EMH suggests that all known information is already reflected in stock prices, so it’s nearly impossible to consistently beat the market.
3. What does diversification mean?
It means spreading your investments across different assets (stocks, bonds) to reduce overall risk while maximising your expected return — a key takeaway from Markowitz’s portfolio theory.
4. What is loss aversion?
A core idea in behavioral finance — people dislike losing money more than they enjoy making it.
5. How can I use these theories as a beginner?
You can use Traditional Finance to structure your portfolio and Behavioral Finance to become aware of your emotions and manage them to improve your chances of success..
6. Who are the most influential researchers in finance?
John Stuart Mill, Harry Markowitz, Eugene Fama, Daniel Kahneman, and Amos Tversky are foundational thinkers in this field.



Great overview of the academic fields in finance — this really helps study abroad aspirants understand core concepts like traditional vs behavioural finance and how they shape modern investment thinking! As someone preparing for global programs, it’s equally important to strengthen language skills alongside academic knowledge. Practising with a TOEFL mock test and consistent IELTS speaking test practice can boost confidence and improve your chances of securing admission and scholarships abroad.
Great insights on finance specializations! I especially liked how you explained the differences between corporate finance, investment banking, and financial analysis. For students planning to study abroad in finance, improving English skills is crucial. I’d recommend checking out the best IELTS coaching in Jaipur to prepare effectively.
Exploring academic fields in finance helps students build strong analytical, quantitative, and strategic skills essential for careers in banking, investment, and global financial markets. Understanding these core areas allows learners to make informed academic and career decisions as they move forward. For those aiming to study abroad, focusing on the Swinburne University acceptance rate becomes crucial when planning applications, as it helps students prepare better and improve their chances of securing admission at a reputed global institution.
Also Read: top 10 courses in demand in abroad
Exploring academic fields in finance opens doors to diverse career paths and advanced studies. Outstanding students can further enhance their prospects by aiming for prestigious opportunities like a harvard scholarship.